Emotional Artificial Intelligence – An Overview
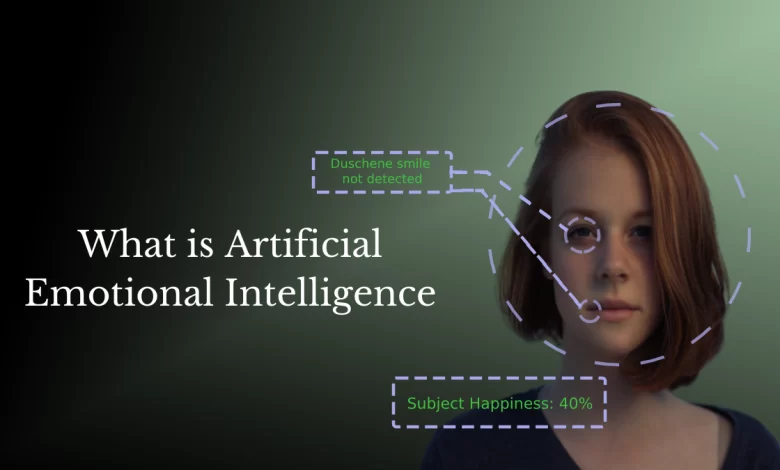
Emotion AI, also known as affective computing, is a rapidly developing area of artificial intelligence that essentially involves machines learning to read and comprehend non-verbal cues given by people, such as their tone of voice, body language, and facial expressions, in order to ascertain how they are feeling. In order to decipher a person’s feelings, these emotional algorithms are able to identify important facial features such as their eyes, eyebrows, cheeks, nose, and so forth. They can then track these features as they move.
Many businesses are using emotional artificial intelligence as a popular trend, successfully seizing the chance to use self-awareness as a tool for building relationships with both customers and staff. In an effort to deepen their interactions with their customers, businesses have been putting more effort into incorporating the deeply human experience of being able to interpret, control, and recreate emotions into their systems.
Emotionally intelligent AI is becoming increasingly important as the use of AI in all industries continues to grow. Programmers in many sectors are searching for new avenues and applications to incorporate emotional intelligence into their products, from chatbots to virtual assistants.
Programmers are investigating ways to enable automation to interact with the audience’s lived experience in addition to improving our current lives through automation. This is where the concept of Emotional Artificial Intelligence comes into play.
For more than ten years, big tech companies and small startups have been utilising emotion AI by applying computer vision or voice analysis to detect human emotions. Companies first obsess on market research before moving on to analysing and measuring people’s emotions to understand how they would react, example, to a certain product or TV ad. Additionally, the science of emotion artificial intelligence is being economically repurposed in call centres, robotics, automobiles, smart devices, and virtual personal assistants.
How Does Emotional AI Work?
Voice assistants may miss cues such as irony, laughter, anger, or irritation because they are primarily trained to answer standard questions. The answer here is emotion AI, which solves this by identifying and understanding emotional metrics and inflection in a specific voice to determine the interaction’s meaning.
These systems are equipped with capabilities that enable them to fully understand the 50 shades of emotion that people incorporate into their voice patterns. They can also calculate and maintain an updated representation of any changes in speech, pitch, timbre, volume, or lengthened pauses. Even a small number of words can directly affect meaning through prosody.
Emotion AI is able to create a whole new map of the meaning behind an interaction, going far beyond the literal meaning of words. It does this by taking into consideration colloquialisms, different key phrases, clauses used in the interaction, and even non-linguistic sounds made by individuals.
In essence, these systems work by collecting behavioural signals related to feelings, expected thoughts, spoken behaviours, concepts, and beliefs. For example, in just a few seconds, one eye roll can convey a very large amount of information. Usually, an eye roll is accompanied by a small sigh or pause in speech. Emotion AI is able to quickly identify and list these changes.
Applications of Emotional AI
Emotion AI providers have expanded into whole new markets and sectors in recent years, helping businesses save significant money while also improving customer experiences. For example, the term “emotion AI,” or emotional artificial intelligence, frequently evokes images of humanoid robots doing customer service tasks, such as the realistic “receptionist” who greets visitors to a Tokyo hotel.
According to a recent article by E&T Magazine, artificial intelligence (AI) has been developed with the ability to interpret wireless signals and reveal people’s inner feelings.
Researchers at Queen Mary University of London have found that, in the absence of additional facial cues, using radio waves to measure respiration and heart rate can be a useful method of forecasting someone’s emotional state. The Queen Mary University of London team’s article, which was also published in the online journal PLOS ONE, explains how a neural network may be used to interpret emotions acquired through radio antenna transmission.
Some of the applications of emotional artificial intelligence are listed below. These consist of:
-
Recognising Mental Strain
In order to help emergency personnel stop suicides and save lives, emotion AI can be used to recognise suicidal ideation. Facebook, for example, uses emotion AI to monitor user posts, search for information that raises a red flag or indicates a person may be suicidal, and notify relevant authorities.
-
Computer Games
Through the use of computer vision, the gaming console or video game recognises the player’s emotions from their facial expressions while they are playing and responds appropriately. Nevermind is one video game example of this type.
-
Learning
Prototypes of learning software have been developed to measure and adapt to children’s emotions. When a youngster shows signs of irritation because a job is too easy or too complicated, the programme adjusts the activity to make it harder or less difficult. Children with autism benefit from another learning system that helps them recognise the emotions of others.
-
Chatbots
Chatbots are designed to quickly and more accurately guide users to the right service flow while taking into account their emotional state. For example, if the system detects that a user is angry, it will either route them to a human or to another escalation flow.
-
Vehicle Safety
Automakers can use computer vision technology to determine the driver’s emotional condition. It might alert the motorist if they are feeling particularly upset or sleepy.
-
Security Industry
Additionally, the security industry uses Emotion AI to identify individuals who are agitated or worried. For instance, the British government uses social media to track its citizens’ opinions on certain subjects.
-
Advertising
Emotional AI is also being used in marketing. Entropik Tech, an AI startup focused on emotion recognition and based in Bengaluru, helps marketers create compelling emotional takeaways that will resonate with their target audience and increase the conversion rate of their high ROI advertising campaigns. The software startup launched an AI-driven platform in August 2019 that uses deep learning and AI algorithms to anticipate consumer mood indicators.
-
Human Capital
Businesses’ HR departments may use Emotion AI to monitor candidates’ stress levels and interactions during interviews, which helps them make better hiring decisions and do HR analytics.
Across industries, emotional artificial intelligence is already widely used. In a variety of industries, including customer service, training, healthcare, financial interactions, and education, systems that are able to recognise and process human facial expressions and voice cues are being used.
Even as it’s clear that human agents won’t be replaced by robots anytime soon, we are seeing an increase in the number of support tools that improve these interactions, enrich surface-level arrangements, and highlight the most common interactions in these situations. At the core of these new technologies is emotion artificial intelligence.
